Geographical coordinates, namely Longitude and Latitude, help determine the exact location of any place on Earth. These are angular measurements, expressed in degrees, which uniquely define points on the planet.
Download notes of Geography as a discipline UPSC Notes
Latitude
Latitude refers to the angular distance of a point north or south of the Equator. These lines run parallel to the Equator and are also known as parallels of latitude.
- Total Degrees: 180° (90° North to 90° South)
- Distance Between Each Degree: Approximately 69 miles (110 km)
Important Parallels of Latitude:
- Equator (0°) – Divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
- Tropic of Cancer (23½° N) – Northern Hemisphere.
- Tropic of Capricorn (23½° S) – Southern Hemisphere.
- Arctic Circle (66½° N) – Marks the beginning of the North Polar region.
- Antarctic Circle (66½° S) – Marks the beginning of the South Polar region.
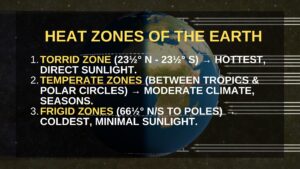
Heat Zones of the Earth
Based on latitudinal positioning, the Earth is divided into three major heat zones:
- Torrid Zone: Lies between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. It receives direct sunlight and experiences the highest temperatures.
- Temperate Zones: Lie between the tropics and the polar circles. These regions experience moderate temperatures.
- Frigid Zones: Located between the Arctic Circle & North Pole and Antarctic Circle & South Pole. They receive minimal sunlight and remain cold throughout the year.
Longitude
Longitude refers to the angular distance east or west of the Prime Meridian. Unlike latitude, these lines are semicircles that converge at the poles.
- Total Degrees: 360° (180° East and 180° West)
- Prime Meridian (0°): Passes through Greenwich, UK, and is the reference for Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
- International Date Line (IDL): Located at approximately 180° longitude, it marks the boundary between calendar days. The line zigzags to prevent confusion across nations.
Longitude and Time
- The Earth completes one rotation (360°) in 24 hours, meaning it moves 15° per hour.
- Moving eastward: Time advances by 1 hour per 15°.
- Moving westward: Time decreases by 1 hour per 15°.
- Countries spanning large longitudinal distances, like Russia, Canada, and the USA, have multiple time zones.
Indian Standard Time (IST)
India follows IST, based on 82½° E longitude. It helps maintain uniformity in time across the country, avoiding multiple time zones.
Download notes of History, Types of History and Historical Sources
FAQs related to Longitude and Latitude
Q1. What is the difference between longitude and latitude?
A. Latitude measures the distance north or south of the Equator, while longitude measures the distance east or west of the Prime Meridian.
Q2. Why is the Prime Meridian important for time zones?
A. The Prime Meridian (0°) is the reference for Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). Since the Earth rotates 360° in 24 hours, every 15° longitude represents a one-hour time difference.
Q3. What are the major heat zones of the Earth?
A. The Frigid Zones (coldest), Torrid Zone (hottest), and Temperate Zones (moderate climate).
Q4. Why is the International Date Line not straight?
A. To prevent dividing countries or islands into different dates, the IDL zigzags in certain places.


